Penetration Testing: What is it?
Table of Contents
- What is penetration testing?
- How penetration testing is done
- How to choose a penetration testing company
- How NetSPI can help
Penetration testing enables IT security teams to demonstrate and improve security in networks, applications, the cloud, hosts, and physical locations. In this guide, learn what penetration testing is, how penetration testing is done, and how to choose a penetration testing company.
What is penetration testing?
Penetration testing, also called pentesting or pen test, is a cybersecurity exercise in which a security testing expert, called a pentester, identifies and verifies real-world vulnerabilities by simulating the actions of a skilled threat actor determined to gain privileged access to an IT system or application.
Penetration testing simulates the actions of a skilled threat actor determined to gain privileged access.
A pentester uses expertise, creativity, and pentesting tools to gain access to IT systems to demonstrate how a threat actor could access IT resources or breach sensitive data. Pentesters are also called vulnerability assessors, white hat hackers, and ethical hackers for hire.
A penetration testing service, also called a pentesting company, identifies vulnerabilities in IT systems that pose real-world risk to the client’s systems. Pentest companies use automated vulnerability assessment tools in the discovery phase as a precursor to manual penetration testing. Scanning tools help penetration testers pick the most promising targets to use in a series of incremental manual steps to gain privileged access.
It is important that penetration testing activities do not break the environment. Sometimes pentesters work against live production systems, and sometimes they work against sandbox environments, depending on the goals of the test, the availability of a sandbox environment, and the potential impact on the production system.
Pentesting is performed with or without privileged credentials, depending on the objectives of the test. Penetration testing was historically performed from the perspective of an unprivileged or anonymous user. Today, the deepest dive into an application may require privileged login access, the actual software code for visual review, and control of the operating system hosting the application.
Although a penetration test is sometimes called a vulnerability assessment, many security vulnerability assessments use only automated scanners and do not simulate a skillful, determined human attacker. Pentesting also differs from a dynamic scan, which only uses vulnerability scanning technologies and not human intuition. Penetration testing is also different from what many software developers call a security test or security assessment, which is often a secure code review or static application security testing.
Benefits of penetration testing
The primary benefit of penetration testing is to inform security efforts to proactively harden the environment. Penetration testing reveals an organization’s security weaknesses. Penetration testing rates and prioritizes vulnerabilities by severity of outcome factored against the likelihood of such an attack.
Additional benefits of penetration testing include:
- Deliver secure software for less money: Security gaps remediated earlier in the software development life cycle (SDLC) cost less to fix than problems found later. Despite best efforts, security vulnerabilities slip through software testing processes. Unlike secure code review, which identifies code that might be exploitable, the vulnerabilities identified by a penetration test are proven to be exploitable.
- Avoid breaches: Discover vulnerabilities and exposures proactively, so you can remediate them and prevent an attack—and avoid the costs of downtime and clean-up resulting from a breach. In addition, you preserve the organization’s good reputation and protect relationships with business partners.
- Use human insight like attackers do: Only a penetration tester (or a malicious attacker) can chain together seemingly low-risk events to verify which vulnerabilities enable unauthorized control. Threat actors adapt to a given environment, so security testers need to adapt, too. Understanding the implications of vulnerability scanner results to a specific application or organization requires human insight.
Pentesters chain together seemingly low-risk events to verify which vulnerabilities enable unauthorized control.
- Achieve compliance: Meet security testing requirements from a third-party authority. Penetration testing is required to demonstrate cybersecurity and achieve compliance with regulations and industry standards, such as the payment card industry (PCI) security standard and the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA).
- Eliminate false positives: Automated scans often report what appears to be a huge security hole in the infrastructure, but isn’t. Or a security gap exists, but the test results lack key information to enable remediation. Manual attacks help the organization avoid spinning its wheels dealing with inaccurate or incomplete vulnerability assessment data.
- Focus remediation: Prioritize remediation for the most important vulnerabilities and receive helpful guidance, such as how to remediate specific vulnerabilities and instruction.
- Demonstrate business impact: Knowing the business impact of vulnerabilities helps justify security investments and improve decision making. Penetration testing clarifies the business impact of inaction.
- Augment the IT security team: A fresh set of eyes from third-party security experts can help strengthen an organization’s vulnerability management program and validate its ability to protect the business from cyber attacks.
Pentesting trends
Four security and development trends are increasing the complexity of penetration testing and changing expectations.
Shift left: Teams are introducing secure code review (SCR) and penetration testing into the software development life cycle (SDLC) to identify vulnerabilities earlier. Called shift left, this software development trend reflects efforts to improve software security and reduce testing costs.
DevSecOps: To ship secure software faster, organizations are working to integrate security processes seamlessly into the software development workflow and CI/CD pipelines. DevSecOps is driving requirements for continuous and comprehensive penetration testing.
Differentiation: Now that many people know about penetration testing, the discussion is changing to highlight differences in penetration testing methodologies, scopes of engagement, and report delivery methods.
Penetration Testing as a Service (PTaaS): This new penetration testing delivery experience shares pentest results with the client in real time through a technology platform or web portal. Pentesting as a service delivers results year-round, unlike point-in-time pentests, which are typically executed just once a year. A PTaaS platform improves decision making and accelerates remediation with tool integration.
Traditionally, pentesters complete an engagement and hand off a penetration testing report in a static PDF or excel spreadsheet. With the emergence of PTaaS, the pentesting firm is an IT security partner that provides continuous vulnerability scanning, conducts deep-dive manual tests as needed, and delivers real-time pentest reports in an interactive digital platform that separates critical vulnerabilities from false positives (a time-consuming activity for an in-house team). The pentesting experts continue to serve the client as remediation consultants.
Types of penetration testing
The targets of penetration testing include networks, software applications, the cloud, and employee behaviors. Each type of penetration test focuses on a different target:
Network penetration testing
Network penetration testing, also called network security testing, focuses on internal and external networks, wireless endpoints and wireless networks, email phishing, and other types of social engineering. Five types of network penetration testing are:
- External penetration testing
- Internal penetration testing
- Mainframe penetration testing
- Wireless penetration testing
- Host-based penetration testing
Application penetration testing
Application penetration testing, also called application security testing, focuses on web and non-web applications, finding vulnerabilities such as those described in the OWASP Top Ten and the CWE/SANS Top 25 Most Dangerous Software Errors. Unlike dynamic application security testing (DAST), which is usually automated, penetration testing is performed by an expert pentester. Four types of application penetration testing are:
- Web application penetration testing
- Mobile application penetration testing
- Thick client application penetration testing
- Virtual application penetration testing
Cloud penetration testing
Cloud penetration testing focuses on cloud infrastructure. A cloud platform can create exposure from network, application, and configuration vulnerabilities that can result in external access to company credentials, internal systems, and sensitive data. The three most common types of cloud penetration testing are:
Adversary simulation and red teaming
Adversary simulations, also known as red team simulations, are security exercises that assesses a company’s capacity to identify and respond to real-world attack and breach scenarios in real time. Four types of adversary attack simulation are:
- Detective control testing
- Red team security operations
- Social engineering penetration testing
- Ransomware attack simulation
Note that social engineering penetration testing is different from most types of penetration testing in that it assesses the effectiveness of security awareness training by simulating real-world threats through email, phone, and in-person physical penetration testing.
Penetration test reporting
Pages and pages of pentesting data presented in a static Excel or PDF pentesting report are overwhelming, and yet a 100-page PDF is a common format for a penetration testing report.
In contrast, a dashboard is a better type of penetration testing report because it delivers dynamic views of penetration testing results: metrics, trends, project communication, searchable and sortable pentest findings, and instruction to reproduce each vulnerability. With a dashboard, less time is spent by clients analyzing penetration testing reports, and critical and high-severity vulnerabilities are ticketed and remediated sooner.
View an example of NetSPI’s penetration test report.
A penetration testing dashboard delivers dynamic views of pentest findings.
How penetration testing is done
In this section, you’ll learn about penetration testing tools, the phases of penetration testing, penetration testing methodologies, and reasons to use expert penetration testers.
Penetration testing tools
The best pentesters use automated tools throughout the pentesting process. Most penetration testing tools automate common exploits. NetSPI’s open source pentest tools on GitHub help penetration testers automate and understand pentest tasks. The most popular of these penetration testing tools are:
- PowerUpSQL: a PowerShell toolkit for attacking SQL Server
- SQL Injection Wiki: a wiki focused on aggregating and documenting SQL injection methods
- MicroBurst: a collection of scripts for assessing Microsoft Azure security
- PESecurity: a PowerShell module to check if a Windows binary (EXE/DLL) was compiled with security features such as: ASLR (Address Space Layout Randomization), DEP (Data Execution Prevention), and SafeSEH (Structured Exception Handling), Strong Naming, and Authenticode
- Goddi (go dump domain info): a tool that dumps Active Directory domain information
Other types of penetration testing tools enable high-volume scanning for vulnerability discovery and improve the delivery of pentest reports. NetSPI’s Scan Monster™ automates and orchestrates our automated scanning activities, freeing pentesters to do more manual testing. NetSPI’s Resolve™ streamlines penetration testing execution and delivery. The Resolve platform correlates vulnerability data into a single view to make pentest findings more actionable.
Discover NetSPI’s open source penetration testing tools.
Phases of penetration testing
A skilled pentester follows five steps or phases of penetration testing with every engagement.
Step 1: Plan and map the test
The first phase of penetration testing clearly defines the scope and objectives of the penetration test, as well as what tests to perform and in which order. This phase also includes careful preliminary risk planning with continency plans to minimize service disruption.
Step 2: Scan for vulnerabilities
The second phase enumerates suspected vulnerabilities identified by automated scanning tools. Virtually every tool generates false positives (vulnerabilities that don’t really exist), so a vulnerability is only enumerated when it appears across multiple automated tools, not just one tool.
Step 3: Assess the vulnerability results
In the third phase, a pentester analyzes the suspected vulnerabilities using specialized pentesting tools and manual pentesting techniques. The goal in this phase is to identify and validate exploitable entry points.
Step 4: Gain access
The fourth phase verifies high-risk vulnerabilities comprehensively using safe exploitation techniques, such as automated pentesting tools, manual processes, and code injection. Often a goal in this step is to gain privileged access status on a networked device and then pivot between trusted network zones and move unabated from one system on a network to another system in a different security zone on the same network. The pentester fully documents the vulnerabilities that enable each successful exploit.
Step 5: Report findings
The fifth phase reports on the pentest findings ranked by severity with a focus on critical and high-severity vulnerabilities. The report includes step-by-step instructions for how to reproduce the pentester’s exploits so remediators can reproduce and fix them.
Penetration testing methodologies
Security testing requires penetration testing companies like NetSPI to balance creative disruption and methodical, systematic structure to ensure high-quality service. A penetration testing methodology is an approach to pentesting that involves repeatable processes and many checklists. Pentesting methodologies should vary based on the business supported, the IT environment, the attack surface, and the target system or application.
Published penetration testing methodologies and frameworks include:
- Information System Security Assessment Framework (ISSAF)
- Technical Guide to Information Security Testing and Assessment (NIST)
- Open Source Security Testing Methodology Manual (OSSTMM)
- Open Web Application Security Project (OWASP)
- Penetration Testing Methodologies and Standards (PTES)
The type of environment has a big impact on penetration testing methodology. Red teaming or adversary simulation are always, and network penetration testing is nearly always, performed on the production network. In contrast, most application penetration testing is performed in a sandbox or development environment, where a pentester can be more rigorous. We might tune a scanner to simulate 10-20 simultaneous users on a non-production system but only one or two on a production system to minimize impact. Pentesting a production system often limits the test cases to read-only.
Runbooks, checklists, and penetration testing tools ensure broader coverage and a consistent penetration testing approach. A vulnerability found in one client’s environment can be added to a checklist for future tests.
Runbooks, checklists, and pentesting tools ensure broader coverage and a consistent penetration testing approach.
At NetSPI, we build runbooks and checklists for every penetration testing service we offer to codify our penetration testing methodology. We build our proprietary penetration testing methodologies into the Resolve™ penetration testing execution and delivery platform to ensure consistent delivery of service.
Why use expert pentesters
Having the right people on staff for pentesting or contracting with the right trusted partner for the work is the most critical component of any pentesting program. Only certain people have the skills, knowledge, and experience to discipline them to:
- Methodically work through the entire penetration testing process
- Effectively use the necessary tools
- Do the necessary ad hoc research required during testing
- Properly interpret, analyze, and communicate the results
Expertise is essential, because poor tool selection, a testing mistake, or the faulty interpretation of vulnerability scanner or pentest results can lead to a false sense of security. Every member of an expert penetration testing team brings insights about security risk assessments to every project. Innovation is critical, as pentesters must test ever more complex environments and new technologies. A collaborative penetration testing team produces the highest quality work when industry-leading pentesters disseminate expertise throughout the team.
Explore NetSPI’s pentesting blog, a resource for the cybersecurity community written by our expert penetration testers and cybersecurity experts.
How to choose a penetration testing company
The success of your vulnerability management and penetration testing program depends on choosing the right penetration testing partner. In this section, you learn nine criteria to choose the best penetration testing company:
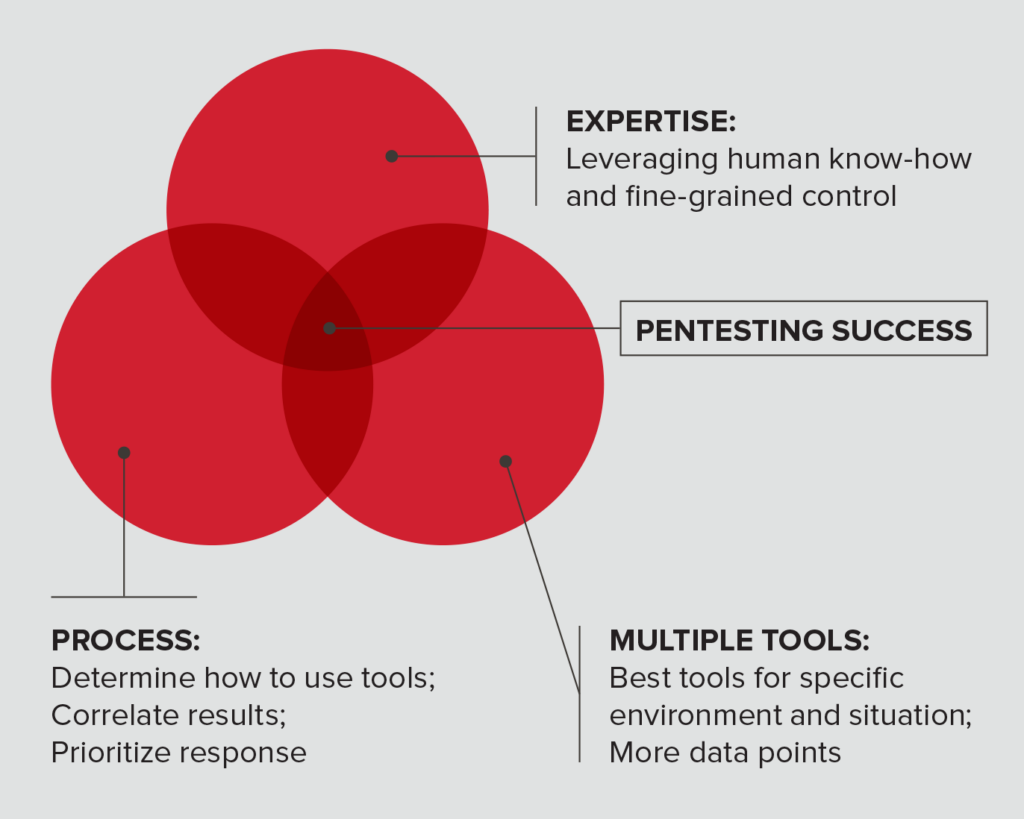
- Prioritize non-negotiables like employing a team of talented and creative deep-dive manual pentesting professionals supported by industry-leading automation technology. Skilled manual testers are essential to every pentesting service, because only a human can identify and verify complex high-severity and critical threats and eliminate false positives.
- Consistent, high-quality processes set the best penetration testing companies apart from the rest. A pentest company that disseminates industry-leading expertise to all its pentesters delivers the best work consistently.
Consistent, high-quality processes set the best penetration testing companies apart.
- Pentest companies need technology to automate and orchestrate recurring tasks, saving time so penetration testers can focus on higher-value tasks. A technology-savvy pentesting company discovers and verifies more high-risk vulnerabilities.
- Insist on real-time reporting that can be easily sorted and acted upon; don’t settle for reams of static PDF reports. Dynamic penetration testing reports make pentest findings more useful and reduce the amount of time your team spends reviewing the reports. A penetration testing delivery platform, like NetSPI’s Resolve™, reports on vulnerabilities the same day they are verified—no waiting.
NetSPI’s Resolve™ pentest delivery platform reports on vulnerabilities the same day they are verified.
- Attackers innovate and so should penetration testing companies. A pentesting vendor should be agile, invest in research and development, and stay ahead of software development and cybersecurity testing trends.
- Look for a penetration testing firm with experience in your industry vertical and other verticals. Real-world experience gained by working with clients in your industry provides immense value.
- Your goals and objectives are unique, so look for custom services. A penetration testing company should scope work and make recommendations according to your needs. Some pentesting companies work with you to find the right balance of how much to invest—based on the system, the type of data and information it supports, its business role, and risk exposure—not a one-size fits all approach.
- Top penetration testing companies can help you mature your application security program. Some penetration testing firms can support your company as it grows, from pentesting to vulnerability management.
- The best pentesting client experience includes a project manager to support you at every phase from scoping to delivery.
How NetSPI can help
NetSPI partners with and provides penetration testing services to nine of the top 10 U.S. banks, three of the world’s five largest healthcare companies, the largest global cloud providers, and many Fortune 500 companies. We offer decades of penetration testing experience across many domains with a focus on best practices and an extremely disciplined process. In this section, you will learn about our industry leadership and deep expertise in penetration testing.
Penetration testing services
NetSPI is the leader in enterprise penetration testing and attack surface management. Our experts perform deep dive manual penetration testing services for application, network, cloud, and other attack surfaces. Our approach is to work closely with your team as a trusted, un-biased advisor with no interest other than the security and health of your network.
We promise a mature, business-centered, and collaborative process with your team. We use multiple best-of-breed tools picked for your unique environmental and targeted needs, in addition to the best, highly skilled penetration testers. We deliver clear, actionable recommendations through our PTaaS service delivery platform that enables our clients to find, track, and fix vulnerabilities faster.
NetSPI finds vulnerabilities that other penetration testing service vendors miss. With NetSPI, you get an experienced penetration testing service team, a project manager, and penetration testers with consistent and proven pentesting playbooks.
Our consultants are also adept at assisting our clients with the development and improvement of penetration testing and vulnerability management programs.
NetSPI finds vulnerabilities that other penetration testing service vendors miss.
Penetration Testing as a Service
NetSPI uniquely delivers Penetration Testing as a Service (PTaaS) through our Resolve penetration testing execution and delivery platform. Clients love PTaaS for the simplicity of scoping new pentest engagements, viewing pentesting report results in real-time, orchestrating remediation, and the security of always-on continuous pentesting services.
PTaaS combines manual and automated ethical hacking attempts with 24/7 scanning, consultation, streamlined communication, and pentest reporting. With NetSPI’s Resolve, you can even import vulnerabilities found by other tools and manual pentesting reports to manage in one place all your company’s vulnerabilities worldwide. Explore the features of PTaaS.
Our industry leadership
NetSPI supports global organizations in protecting and securing their technology and data. NetSPI conducts more than 150,000 hours of testing every year, and we’re changing pentesting entirely. Our people, our processes, and our technology are unrivaled. We make it easier to track trends, track vulnerabilities, and improve your vulnerability management program.
Our security experts notably:
- Author one of the industry’s top security testing blogs
- Develop leading open source pentesting tools
- Are the industry-leading experts in Azure penetration testing
Learn more about penetration testing, cybersecurity, and vulnerability management by exploring our:
Contact Us:
Our team of security testing experts is ready to answer your questions.
Authors:
Explore more blog posts

Navigating Cybersecurity Regulations Across Financial Services
Learn about five areas businesses should consider to help navigate cybersecurity regulations, such as the Digital Operations Resiliency Act (DORA).
A New Era of Proactive Security Begins: The Evolution of NetSPI
Introducing The NetSPI Platform, the proactive security solution used to discover, prioritize, and remediate the most important security vulnerabilities. Plus, get a first look at NetSPI’s updated brand!
Ransomware Prevention, Detection, and Simulation
Your complete guide to ransomware. Learn what ransomware is, how it fuels criminal activity, how it works, and how to stop it.


