Aligned Objectives
Have we defined the cybersecurity objectives that are meaningful to each stakeholder?
CTEM offers a comprehensive resolution to this growing challenge, enabling security teams to stay ahead of continually evolving threats. Through continuous detection and mitigation, CTEM ensures that you can address high-risk vulnerabilities before threat actors exploit them. This proactive approach not only protects critical assets but also builds organizational agility, compliance, and resilience in the face of an uncertain threat landscape.
 Prioritize Critical Threats
Prioritize Critical Threats Strengthen Regulatory Compliance
Strengthen Regulatory Compliance  Build Organizational Agility
Build Organizational Agility Cost Savings & Operational Efficiency
Cost Savings & Operational Efficiency"By 2028, organizations integrating penetration testing into a CTEM program for key applications will be 35% less likely to face disruptive cyber breaches."
Gartner® is a registered trademark and service mark of Gartner, Inc. and/or its affiliates in the U.S. and internationally and is used herein with permission. All rights reserved.
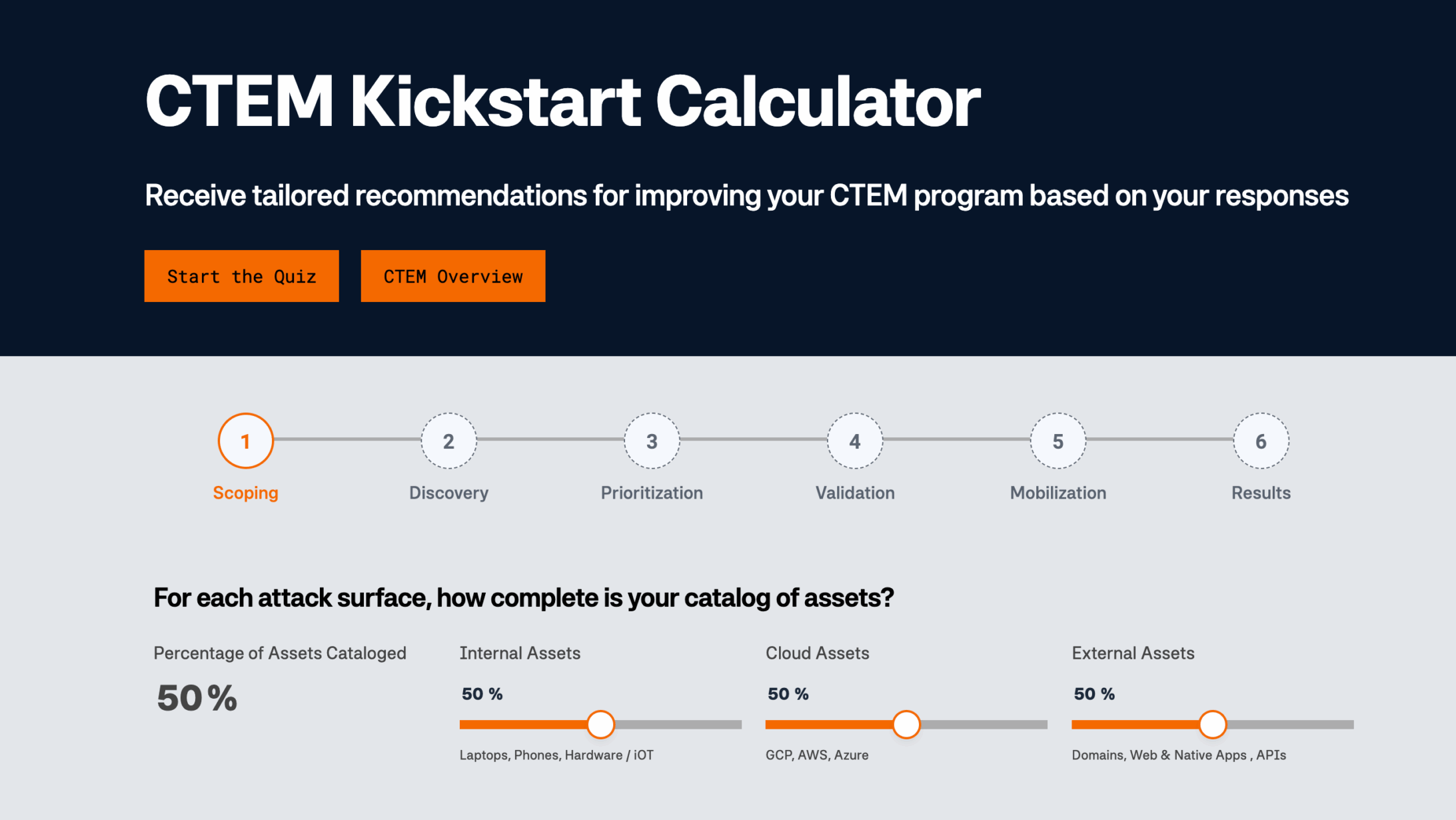
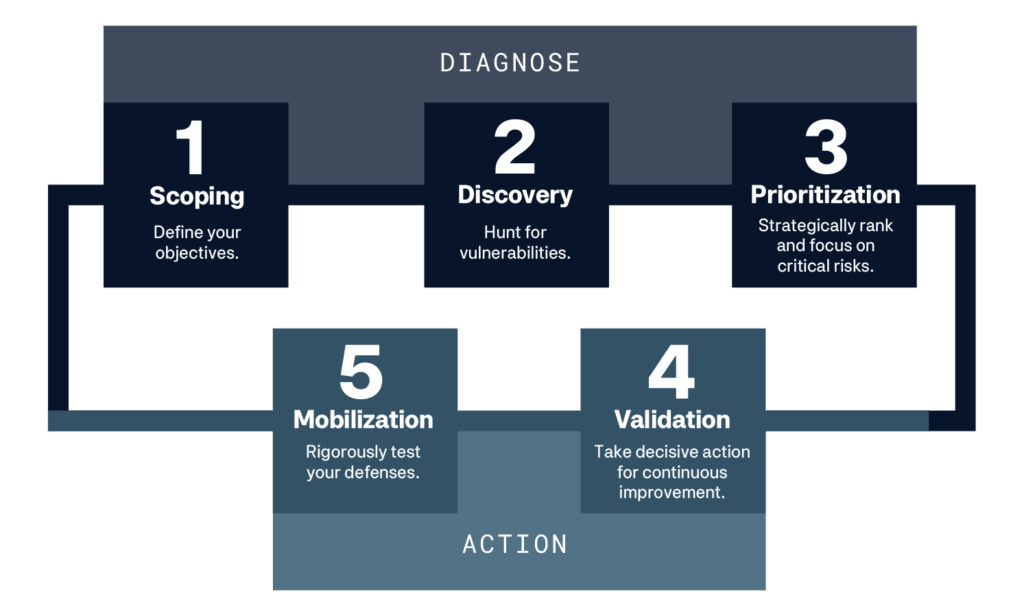
This first phase covers pillars 1, 2, and 3 of the CTEM Framework. This entails defining objectives, inventorying assets, and developing a method for prioritizing vulnerabilities based on technical severity and business impact. A key differentiator of the CTEM framework is collaboration between departments, ensuring alignment between cybersecurity goals and business priorities.
“Who are the key players in our organization responsible for cybersecurity?”
This second phase covers pillars 4 & 5 of the CTEM Framework. This includes validating threats and taking decisive action against the most critical vulnerabilities defined in pillar 3. An unique aspect of the CTEM framework is continuously testing your defenses against Breach & Attack Simulations (BAS) or Red Team Exercises.
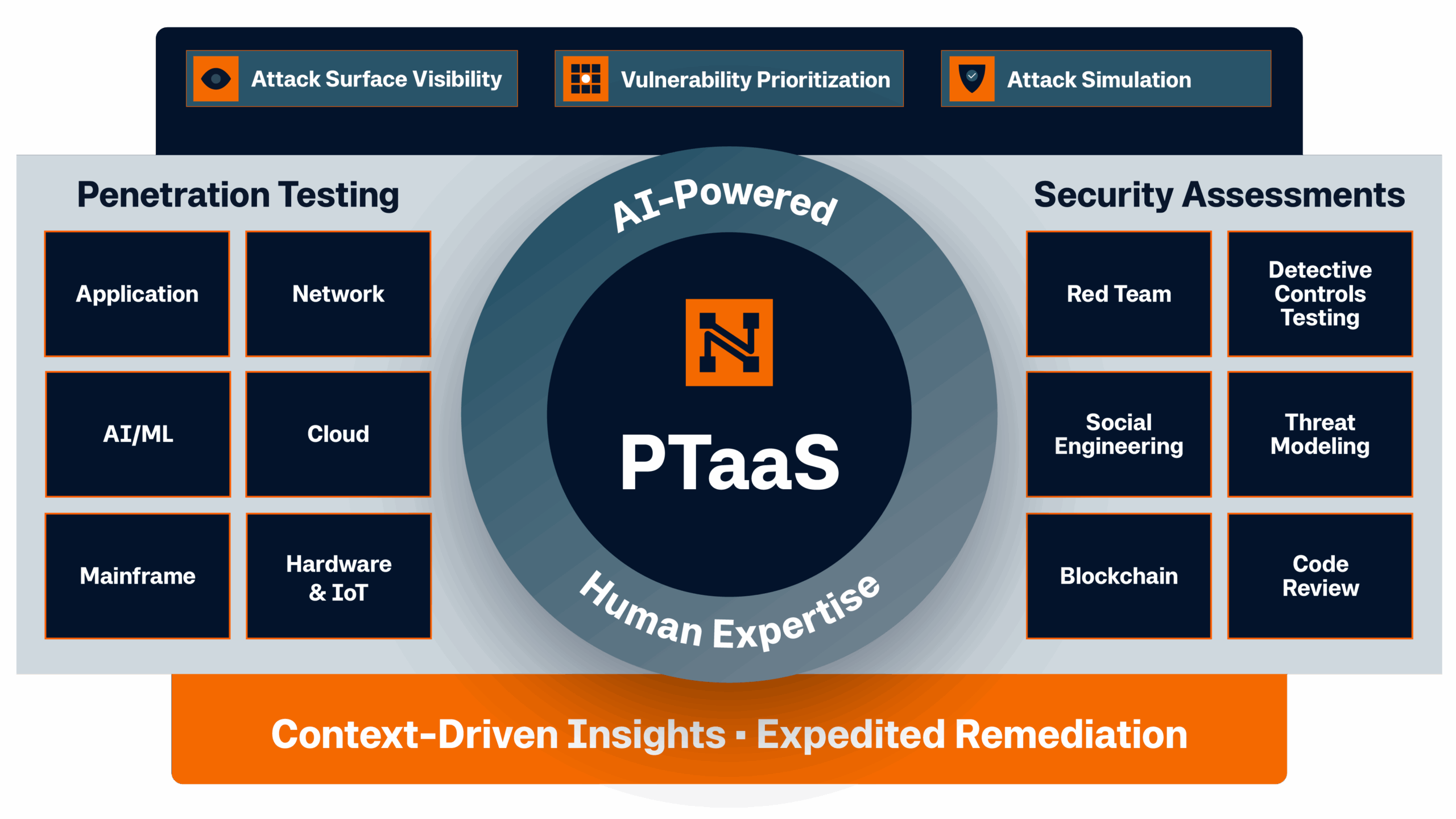
To fully enable a CTEM strategy, security teams can leverage specific technologies and services designed to offer complete visibility and control. NetSPI’s solutions are purpose-built to align with CTEM by seamlessly integrating these advanced technologies into one cohesive platform. This unified approach empowers security leaders with comprehensive insights across their attack surface, enabling them to identify, prioritize, and remediate vulnerabilities efficiently.
“By consolidating these solutions into a single platform, NetSPI enhances the depth, accuracy, and return on investment of cyber threat exposure management.”
Vulnerability Management (VM) has long been the cornerstone of cybersecurity strategies, primarily focusing on identifying and patching known CVEs. A Continuous Threat Exposure Management (CTEM) program goes beyond traditional vulnerability management by providing three additional outcomes:
CTEM emphasizes validating whether identified vulnerabilities and exposures can actually be exploited in your specific environment through methods like attack path modeling, breach and attack simulation (BAS), and Red Teaming.
CTEM aligns security efforts with business objectives by prioritizing remediation based on the actual risk and impact to the organization’s critical assets and operations. This means focusing on exposures that matter most to the business rather than just theoretical risks.
CTEM establishes an ongoing, iterative process for managing threat exposure. It involves continuous assessment, validation, prioritization, and mobilization, ensuring that defenses remain effective against evolving threats. This contrasts with the point-in-time approach of traditional vulnerability management.
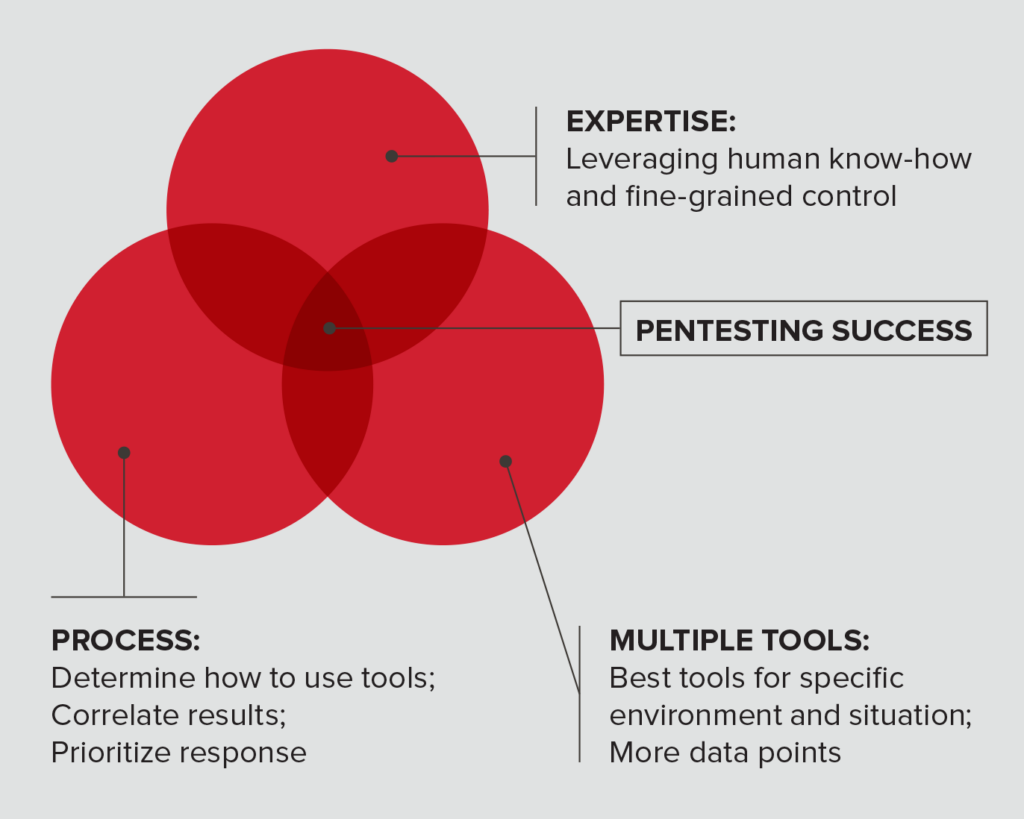
The effectiveness of VM is also diminishing due to an ever growing threat of Non-patchable vulnerabilities on attack surfaces. Non-patchable vulnerabilities include assets such as legacy 3rd Party integrations, mismanaged credentials, poor network architecture, and hardware / embedded systems within your office, data-center, or manufacturing facility. In addition to automated security testing, a mature CTEM program regularly conducts manual tests to determine the exploitability and impact of malicious activities on assets that traditional VM could consider patch-perfect.